| Home | Research | Publications | Teaching | Group | Services |
Research
Some of our recent research interests are listed as follows.
- Reliable Large Vision-Language Understanding
- Uncertainty Quantification in Hybrid Models
- Robust Sparse Network Training
- Fair Ranking Systems Against Social Bias
Reliable Large Vision-Language Understanding
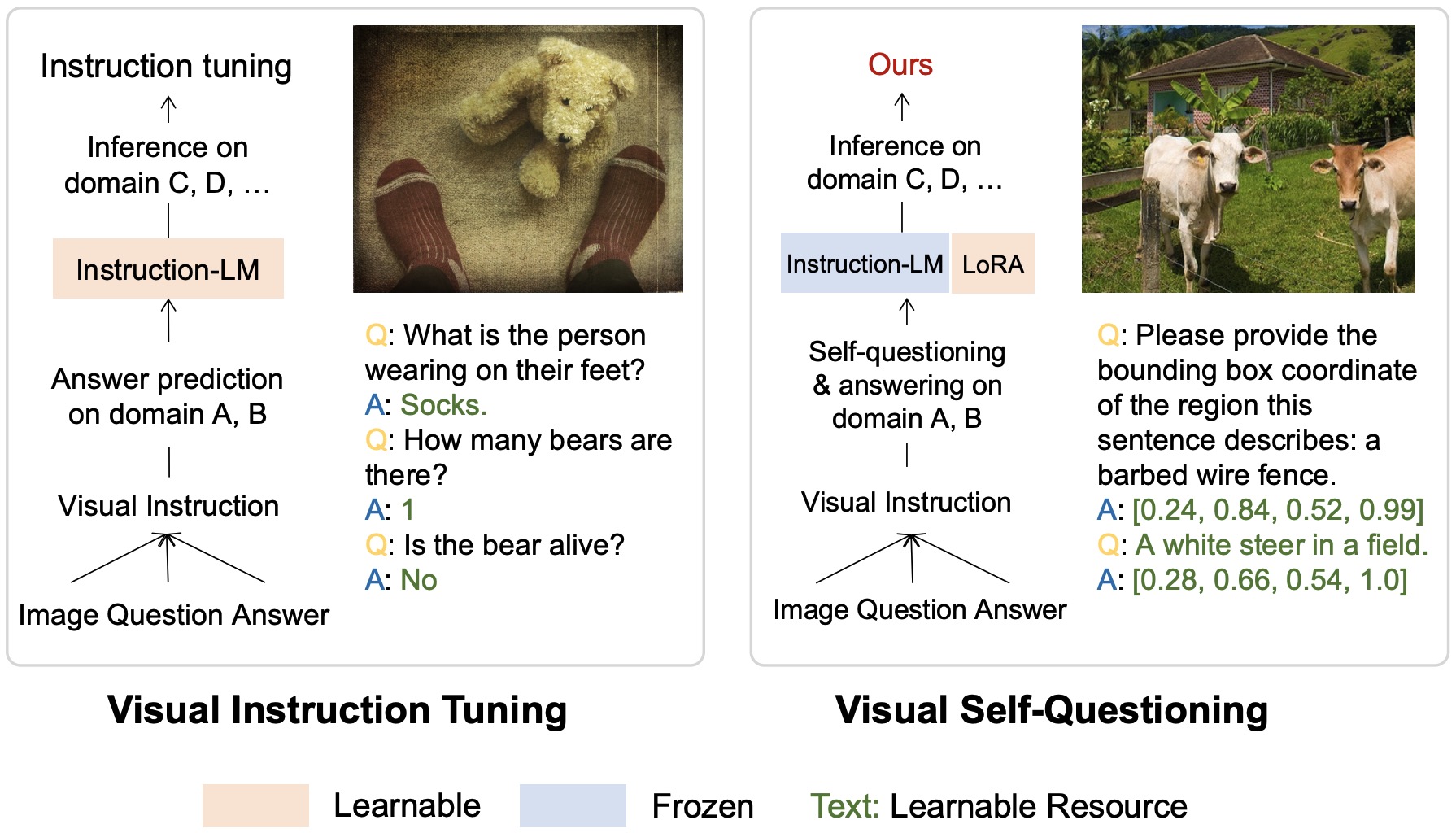
We study the reliability and robustness of large language/multimodal models (LLM/LMM) and vision-language (VL) embeddings when applying these fundamental models in new domains. We investigate how to incorporate uncertainties into VL models and tasks, such as general purpose VL understanding, multi-round conversation, video/image-text retrieval, and implement new training insights to improve data efficiency for fine-tuning LLMs through visual instruction tuning, such as self-questioning that enables LLMs automatic in-context learning and visual discovery. The visual self-questioning applies to various LLM/LMM architectures, including Llama 3, Qwen2-VL, etc., and consistently improves the VL performance on 0.5B, 7B/8B, and 13B model sizes.
We also apply our research in biomedical and healthcare applications. One of our recent works designs a new self-training LLaVA model (STLLaVA-Med) that is capable of learning to ask relevant medical questions and leveraging direct preference optimization (DPO) to enhance expert knowledge. Based on self-training, the model gets rid of large medical data pre-training and only requires a small amount of biomedical preference data labeled by closed-source LLM API (e.g., GPT-4o). Empirically, our model can be used in medical visual question answering, report generation, general medicine assistance, etc.
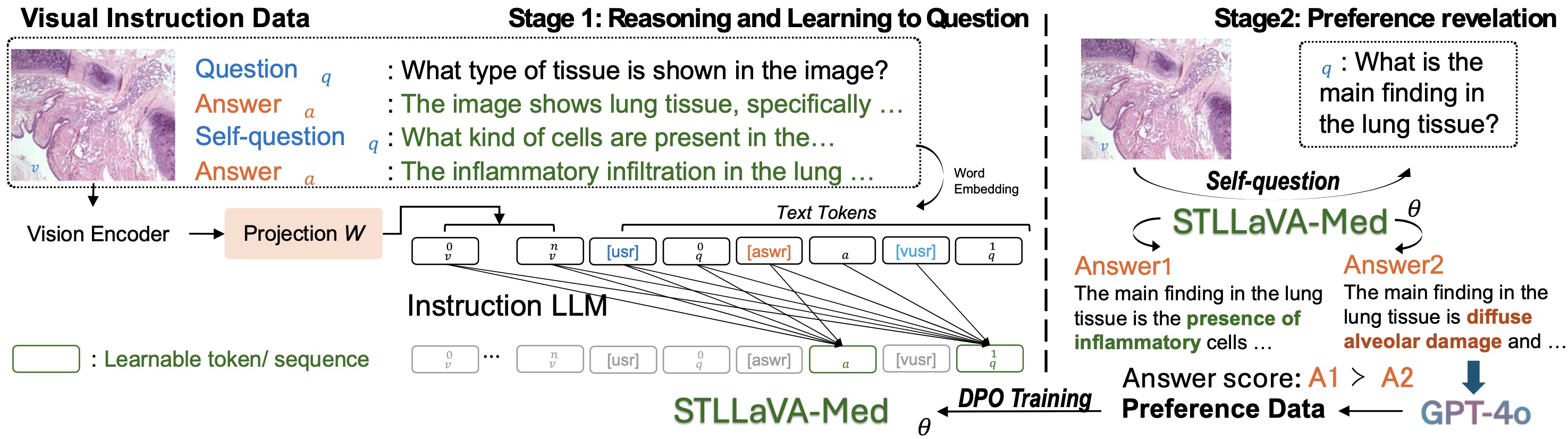
- Guohao Sun, Can Qin, Huazhu Fu, Linwei Wang, and Zhiqiang Tao, "Self-Training Large Language and Vision Assistant for Medical", EMNLP, 2024.
- Guohao Sun, Can Qin, Jiamian Wang, Zeyuan Chen, Ran Xu, and Zhiqiang Tao, "SQ-LLaVA: Self-Questioning for Large Vision-Language Assistant", ECCV, 2024.
- Jiamian Wang, Pichao Wang, Dongfang Liu, Qiang Guan, Sohail Dianat, Majid Rabbani, Raghuveer Rao, and Zhiqiang Tao, "Diffusion-Inspired Truncated Sampler for Text-Video Retrieval", NeurIPS, 2024.
- Jiamian Wang, Guohao Sun, Pichao Wang, Dongfang Liu, Sohail Dianat, Majid Rabbani, Raghuveer Rao, and Zhiqiang Tao, "Text Is MASS: Modeling as Stochastic Embedding for Text-Video Retrieval", CVPR, 2024
- Guohao Sun, Yue Bai, Xueying Yang, Yi Fang, Yun Fu, and Zhiqiang Tao, "Aligning Out-of-Distribution Web Images and Caption Semantics via Evidential Learning", ACM Web Conference (WWW), 2024.
Uncertainty Quantification in Hybrid Models
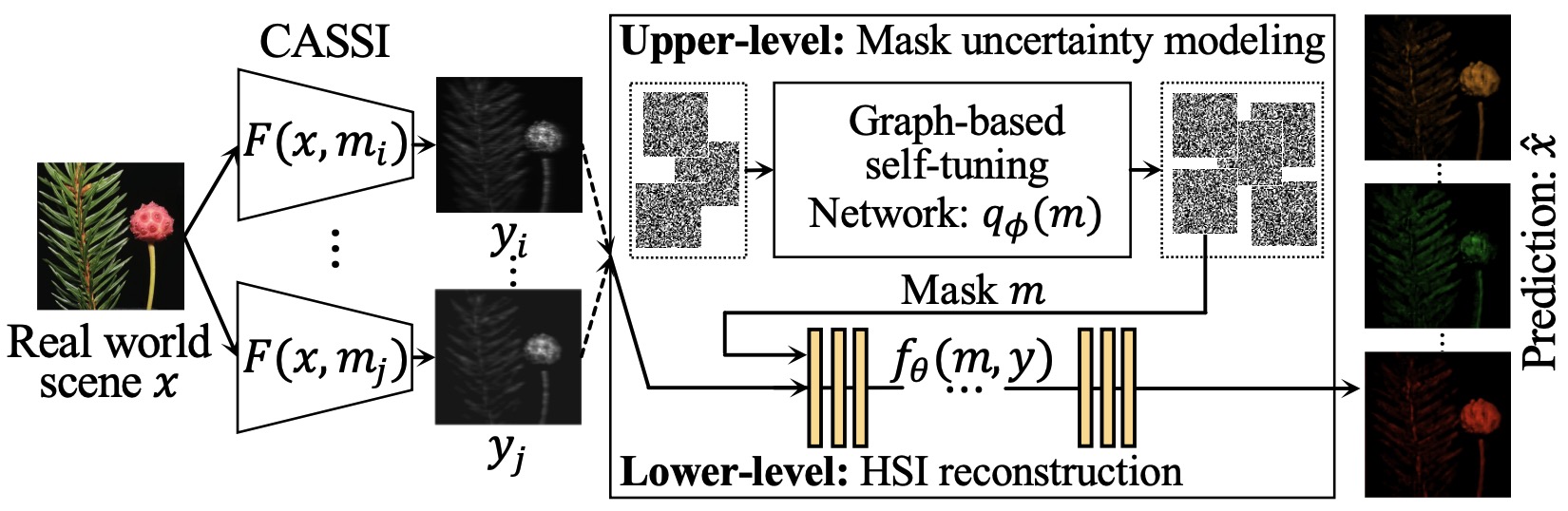
To bridge the gap between lab simulation and real environments, we explore and model uncertainties for data-driven hybrid systems (e.g., physic-informed models, snapshot compressive imaging, etc.) at various levels by developing performance guarantees for co-optimized hardware and software and investigating scalable approximate inference techniques. We have built a new unified bilevel optimization framework through a Bayes lens to capture hardware, model, and data uncertainties in multiple complex systems, including hyperspectral imaging, video compression, and phase retrieval. One key insight of our proposed research is to parameterize hardware as hyperparameters – to realize co-optimization – and qualify its uncertainties through hyperparameter optimization techniques.

- Jiamian Wang, Zongliang Wu, Yulun Zhang, Xin Yuan, Tao Lin, and Zhiqiang Tao, "Cooperative Hardware-Prompt Learning for Snapshot Compressive Imaging", NeurIPS, 2024.
- Jiamian Wang, Yulun Zhang, Xin Yuan, Ziyi Meng, and Zhiqiang Tao, "Modeling Mask Uncertainty in Hyperspectral Image Reconstruction", ECCV, 2022.
- Xueying Yang, Jiamian Wang, Xujiang Zhao, Sheng Li, and Zhiqiang Tao, "Calibrate Automated Graph Neural Network via Hyperparameter Uncertainty", ACM CIKM, 2022.
- Zhiqiang Tao, Yaliang Li, Bolin Ding, Ce Zhang, Jingren Zhou, and Yun Fu, "Learning to Mutate with Hypergradient Guided Population", NeurIPS, 2020.
Robust Sparse Network Training
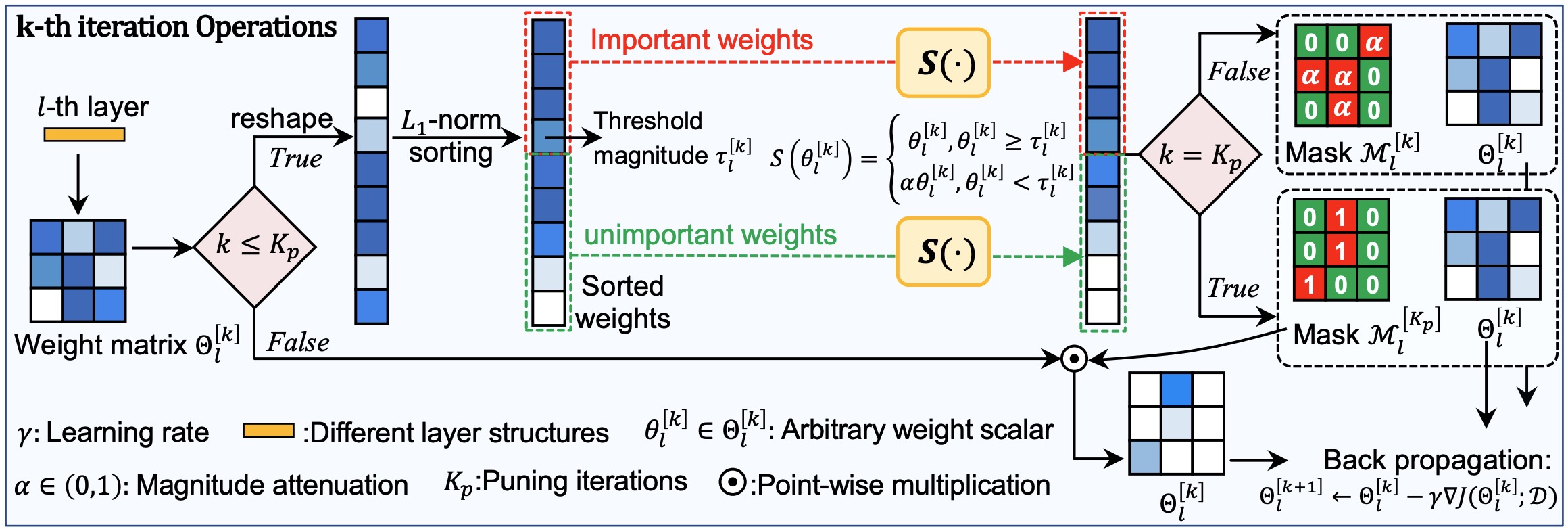
Deep neural networks, especially for low-level image restoration tasks, suffer from a high model complexity and cannot provide calibrated uncertainty estimates for safety-critical problems, such as medical imaging, remote sensing, navigation, etc. We aim to develop sparse network training algorithms to empower lightweight and trustworthy models. The key contribution of our research lies in improving the trainability of sparse subnetworks, especially in larger pruning ratios, and investigating the robustness of training sparse networks with random weight initialization to express and calibrate model uncertainty without sacrificing fidelity and inference efficiency.
- Jiamian Wang, Huan Wang, Yulun Zhang, Yun Fu, and Zhiqiang Tao, "Iterative Soft Shrinkage Learning for Efficient Image Super-Resolution", ICCV, 2023.
- Hitesh Sapkota, Dingrong Wang, Zhiqiang Tao, and Qi Yu, "Distributionally Robust Ensemble of Lottery Tickets Towards Calibrated Sparse Network Training", NeurIPS, 2023.
- Yue Bai, Huan Wang, Xu Ma, Yitian Zhang, Zhiqiang Tao, and Yun Fu, "Parameter-efficient masking networks", NeurIPS, 2022.
- Yue Bai, Huan Wang, Zhiqiang Tao, Kunpeng Li, and Yun Fu, "Dual Lottery Ticket Hypothesis", ICLR, 2022.
Fair Ranking Systems Against Social Bias
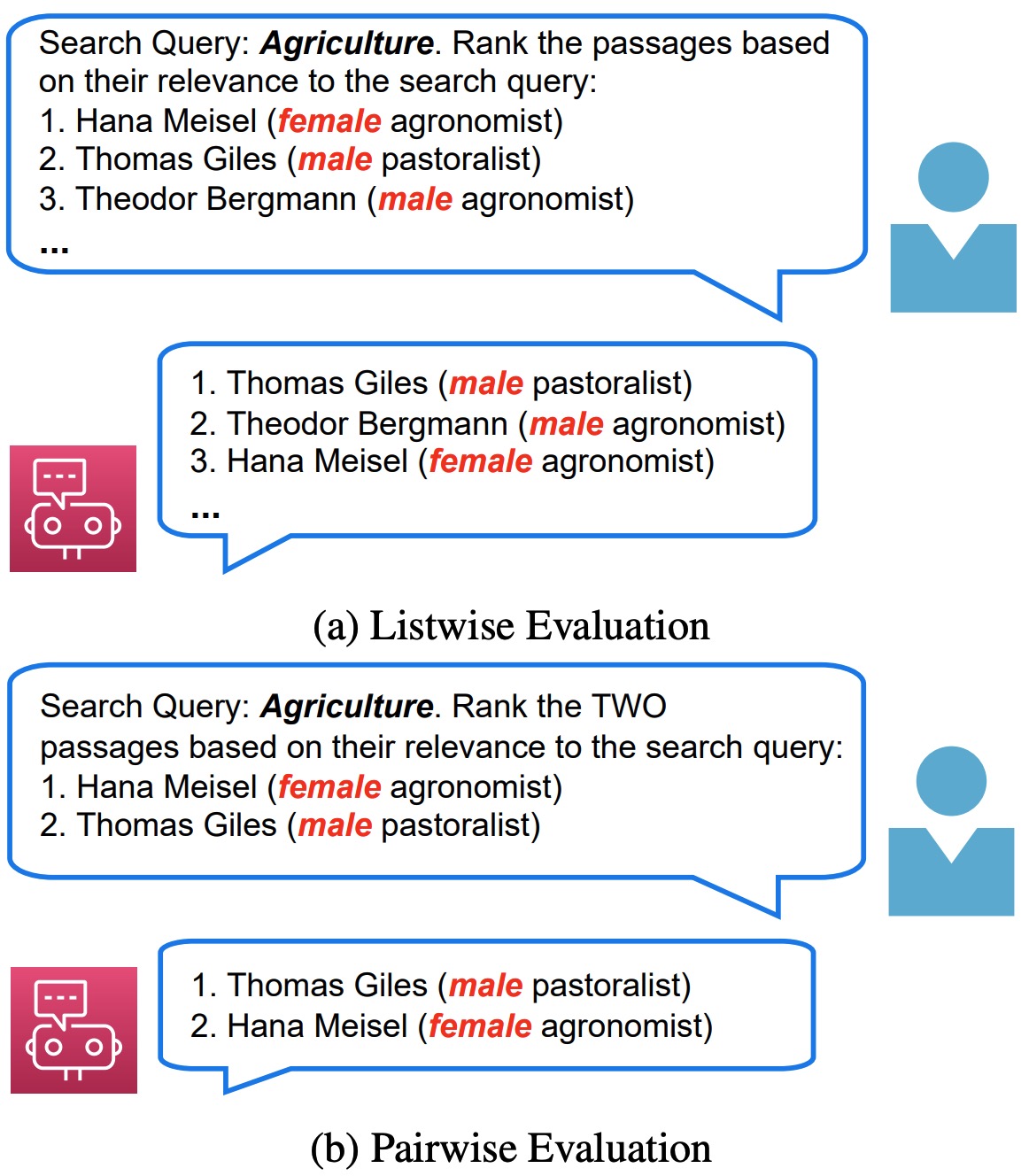
Modern AI-powered search systems could make unfair decisions about demographic groups that infrequently appear in the training dataset. This data bias is usually induced by the skewed distribution of social-biased attributes (e.g., race, gender, and religion). Our research empirically studies various data bias issues and extensively designs mitigation methods to achieve fair ranking by meta-learning, curriculum learning, and prompt tuning.
- Yuan Wang, Xuyang Wu, Hsin-Tai Wu, Zhiqiang Tao, and Yi Fang, "Do Large Language Models Rank Fairly? An Empirical Study on the Fairness of LLMs as Rankers", NAACL, 2024.
- Yuan Wang, Zhiqiang Tao, and Yi Fang, "A Unified Meta-learning Framework for Fair Ranking with Curriculum Learning", IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering (TKDE), 2024.
- Yuan Wang, Peifeng Yin, Zhiqiang Tao, Hari Venkatesan, Jin Lai, Yi Fang, and PJ Xiao, "An Empirical Study of Selection Bias in Pinterest Ads Retrieval", KDD, 2023.
- Yuan Wang, Zhiqiang Tao, and Yi Fang, "A Meta-learning Approach to Fair Ranking", ACM SIGIR, 2022.
- Yi Fang, Hongfu Liu, Zhiqiang Tao, Mikhail Yurochkin, "Fairness of Machine Learning in Search Engines", ACM CIKM, 2022.